The four chemically important types of atomic orbital correspond to values of l = 0, 1, 2, and 3. Orbitals with l = 0 are s orbitals and are spherically symmetrical, with the greatest probability of finding the electron occurring at the nucleus. All orbitals with values of n > 1 and l = 0 contain one or more nodes.
Atomic Orbital – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
An orbital is sometimes thought of a possible region where you can find an electron inside an atom. We know for sure that an electron lies inside this region, but we cannot pinpoint the location of an electron inside of this orbital.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
The boundary surfaces of the p orbitals are shown in Figure 3.All p orbitals are double-lobed, with a region of high electron density on each side of the nucleus. The boundary surface of a p orbital therefore consists of two lobes projecting from the nucleus. The three p orbitals of a given shell are often designated p x, p y, or p z according to the alignment of their lobes along one of three
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Meaning of depiction of atomic orbitals – ECHEMI The quantum numbers n = 1 and ℓ = 0 describe a small spherical wave with no nodes, the quantum numbers n = 2 and ℓ = 0 describe a larger spherical wave with a single node, and the quantum numbers n = 3 and ℓ = 0 describe an even larger spherical wave with two nodes. These waves all look slightly different, as shown in Figure 6.16.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
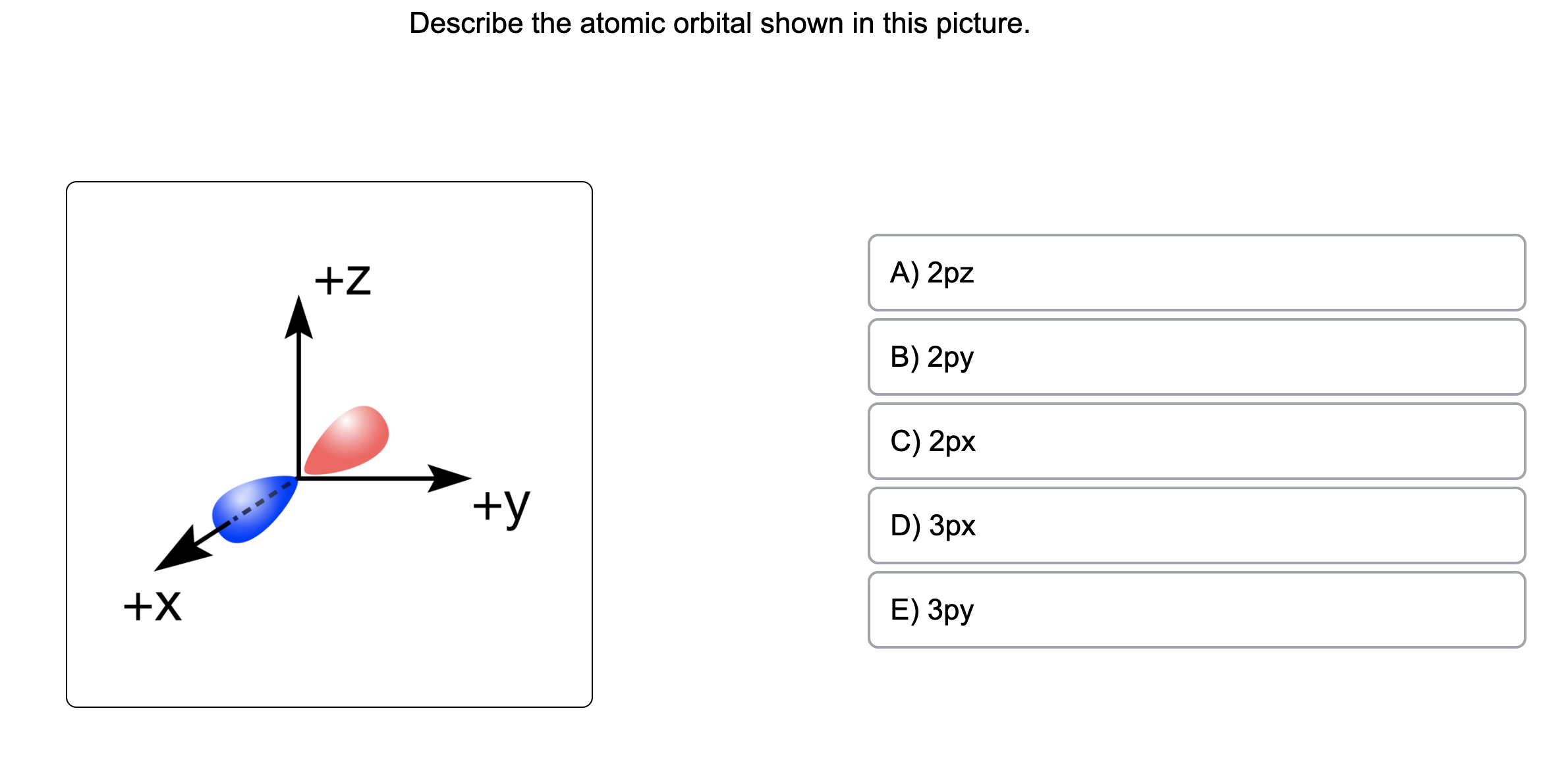
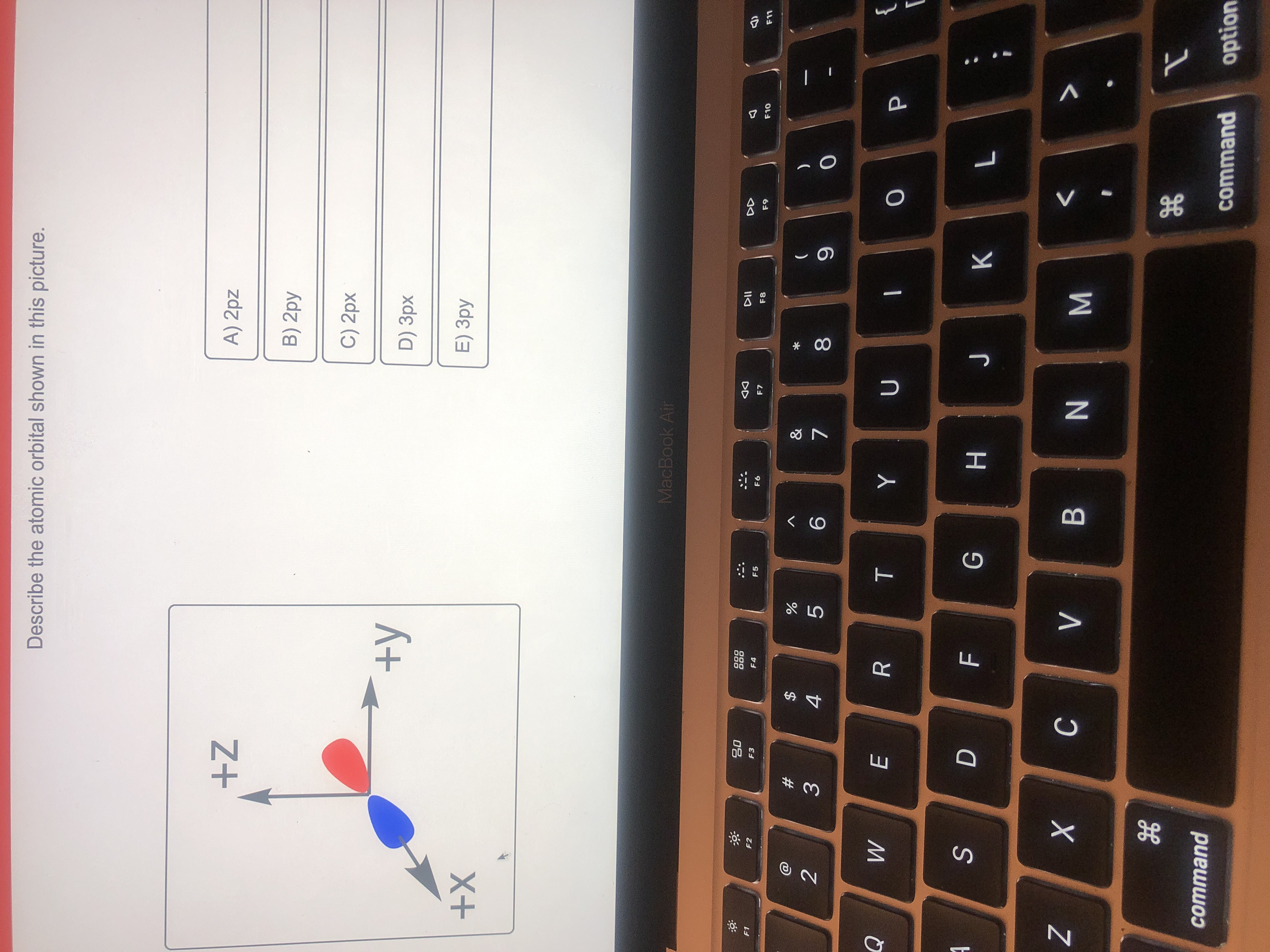
Describe The Atomic Orbital Shown In This Picture
The quantum numbers n = 1 and ℓ = 0 describe a small spherical wave with no nodes, the quantum numbers n = 2 and ℓ = 0 describe a larger spherical wave with a single node, and the quantum numbers n = 3 and ℓ = 0 describe an even larger spherical wave with two nodes. These waves all look slightly different, as shown in Figure 6.16. Nov 9, 202311/09/2023 Chemistry College verified answered • expert verified Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. A) 2pz B) 2py C) 2px D) 3px E) 3py cookiemonster020 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points. plus Add answer +7 pts Expert-Verified Answer No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? 😎 pstnonsonjoku
SOLVED: Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. +Z A) Zpz B) Zpy C) Zpx +y D) 3px +X E) 3py MacboalAr S 2 M 88 J8 command command option
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital ( / ˈɔːrbɪtəl /) is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. [1] This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom’s nucleus. Answered: Describe the atomic orbital shown in… | bartleby
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
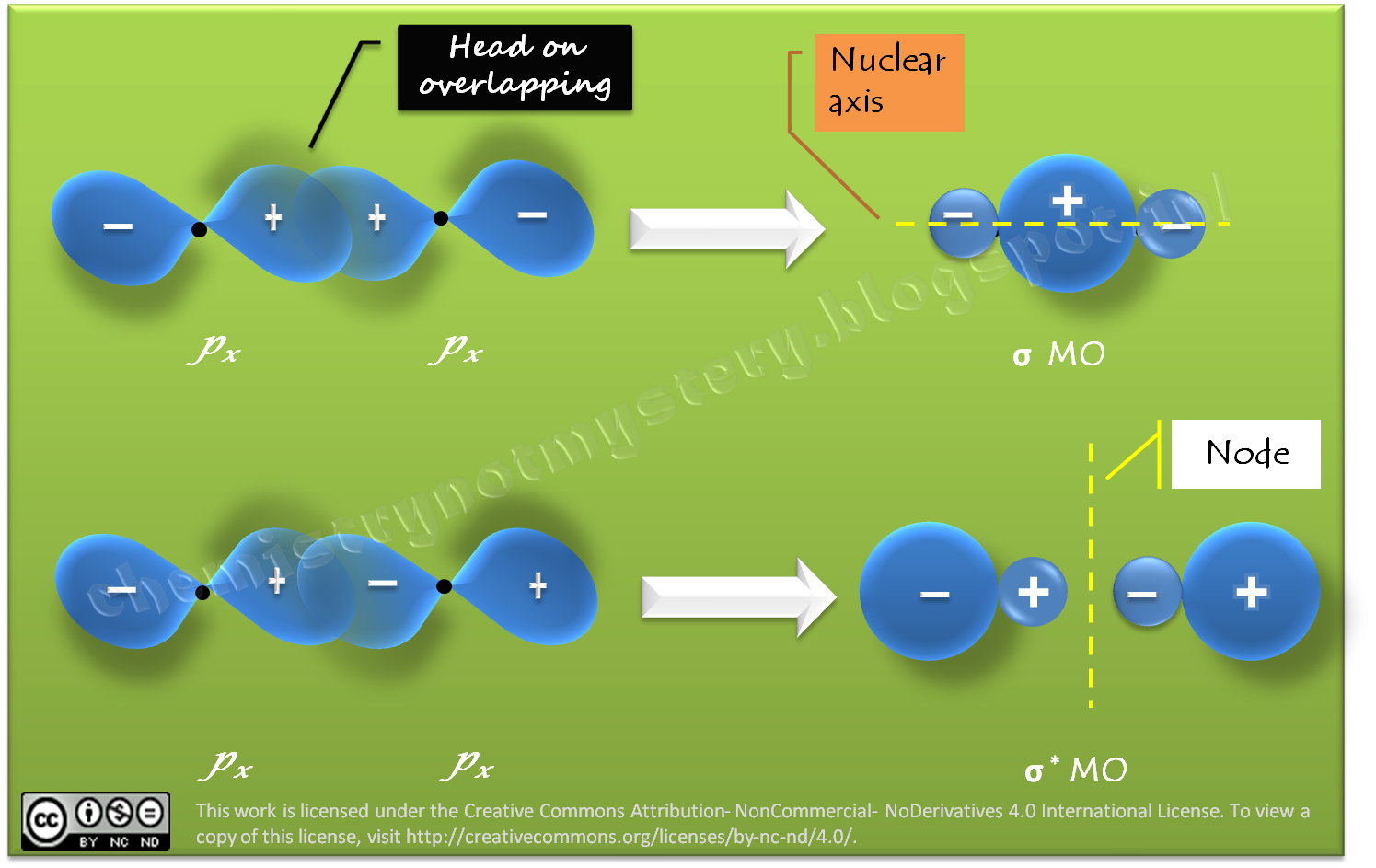
5.5: Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry LibreTexts In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital ( / ˈɔːrbɪtəl /) is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. [1] This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom’s nucleus.
Source Image: chem.libretexts.org
Download Image
Atomic Orbital – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The four chemically important types of atomic orbital correspond to values of l = 0, 1, 2, and 3. Orbitals with l = 0 are s orbitals and are spherically symmetrical, with the greatest probability of finding the electron occurring at the nucleus. All orbitals with values of n > 1 and l = 0 contain one or more nodes.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Meaning of depiction of atomic orbitals – ECHEMI The boundary surfaces of the p orbitals are shown in Figure 3.All p orbitals are double-lobed, with a region of high electron density on each side of the nucleus. The boundary surface of a p orbital therefore consists of two lobes projecting from the nucleus. The three p orbitals of a given shell are often designated p x, p y, or p z according to the alignment of their lobes along one of three
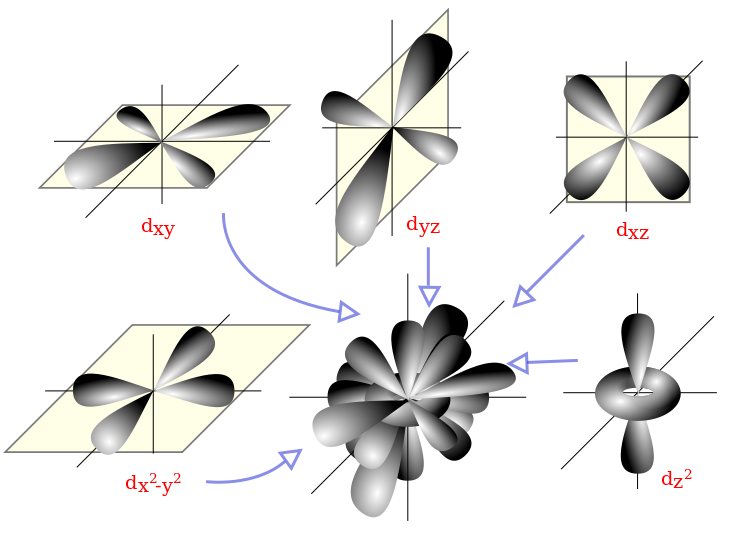
Source Image: echemi.com
Download Image
Molecular Orbital Theory (Cont’d) – Wize University Chemistry Textbook | Wizeprep Show how radial density changes as the radius increases. Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are (energy) states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. If we insist on the particle nature of electrons, then the probability of finding an electron in an atomic orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction.

Source Image: wizeprep.com
Download Image
the order of filling 3d and 4s orbitals The quantum numbers n = 1 and ℓ = 0 describe a small spherical wave with no nodes, the quantum numbers n = 2 and ℓ = 0 describe a larger spherical wave with a single node, and the quantum numbers n = 3 and ℓ = 0 describe an even larger spherical wave with two nodes. These waves all look slightly different, as shown in Figure 6.16.
Source Image: chemguide.co.uk
Download Image
Chemistry!!! Not Mystery : Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals px, py and pz Nov 9, 202311/09/2023 Chemistry College verified answered • expert verified Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. A) 2pz B) 2py C) 2px D) 3px E) 3py cookiemonster020 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points. plus Add answer +7 pts Expert-Verified Answer No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? 😎 pstnonsonjoku
Source Image: chemistrynotmystery.com
Download Image
5.5: Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry LibreTexts
Chemistry!!! Not Mystery : Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals px, py and pz An orbital is sometimes thought of a possible region where you can find an electron inside an atom. We know for sure that an electron lies inside this region, but we cannot pinpoint the location of an electron inside of this orbital.
Meaning of depiction of atomic orbitals – ECHEMI the order of filling 3d and 4s orbitals Show how radial density changes as the radius increases. Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are (energy) states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. If we insist on the particle nature of electrons, then the probability of finding an electron in an atomic orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction.